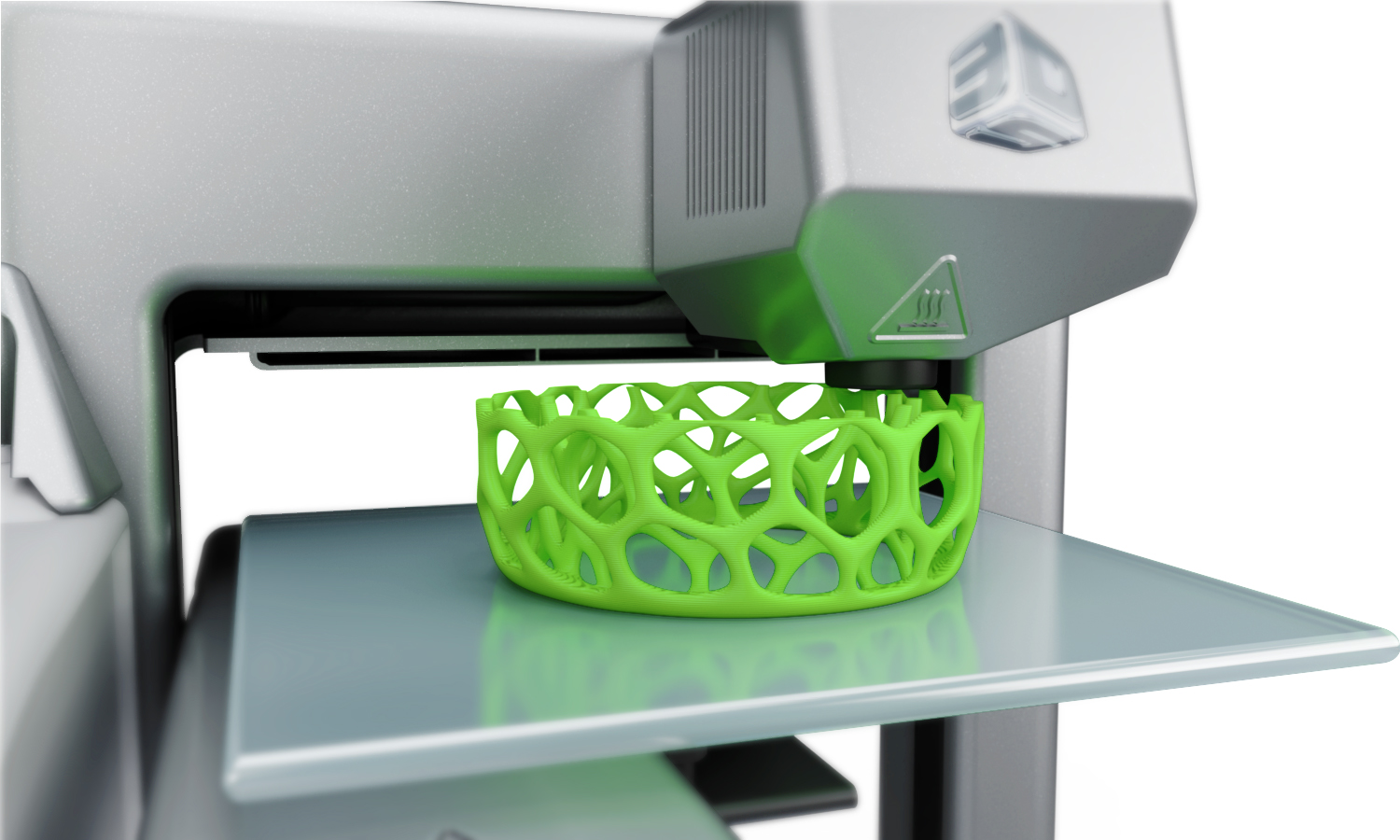
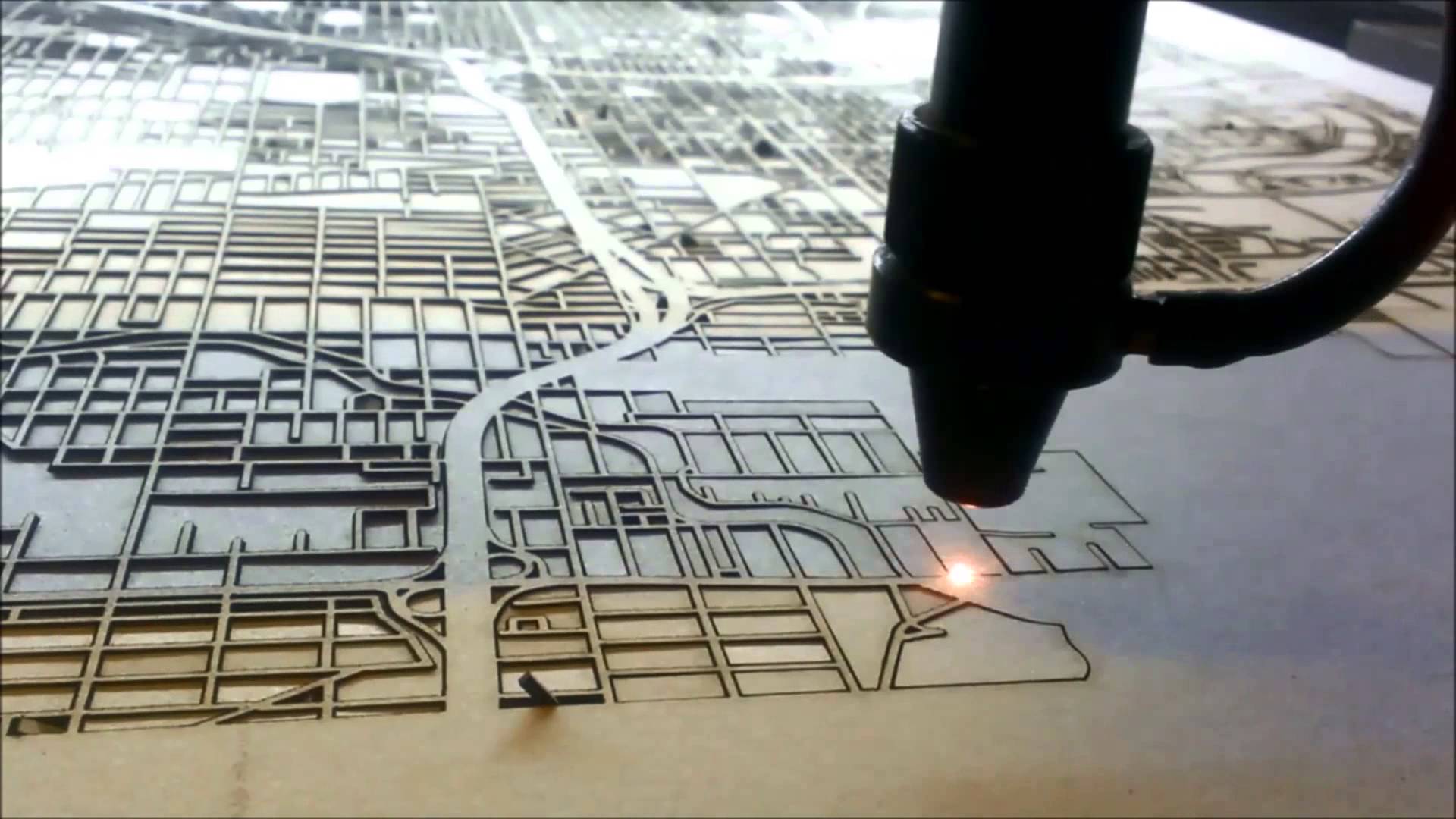
A brief explanation of what is Digital Fabrication and some of its most used terms
Generally speaking, Digital Fabrication is a term used to descibe processes of manufacturing in which the tools used are machines controlled by a commputer.
The Digital Fabrication tools is a great trend in the Architecture field and has emerged in the last years as a revolution in the relation between design and manufacturing. The use of new technologies has allowed perhaps more than in any other period of history the change in the architecture and how building are constructed.
Although the change from analog to digital drawing was a dramatic shift in how the buildings are designed. It has not changed very much how they are built. Basically, this was only a change from one 2D way of drawing to another.
However, the use of Computer not only to draw, but to fabricate as well, has significantly augmented the possibilities to the designers. For the first time, the gap between what was designed and what as built has been reduced to a minimum value. Now, what you draw (or 3D model) is basically what you manufacture. And this has allowed not only more faithful prototypes, models and buildings, but also has stimulated architects to experiment new uses of these technologies, creating new forms and ways to manufacture that couldn’t be tried before. In the next posts I will show some examples of buildings and models that made use of these new possibilities.
Common Terms:
Some terms are used constantly in the field of Digital Fabrication. Thus they will b recurrent in the next posts, so, to make easier to understand, I will post the definition of some of the most used terms, and if I feel that others needs to be better explained, I will make a dedicated post those explaining in detail them.
-
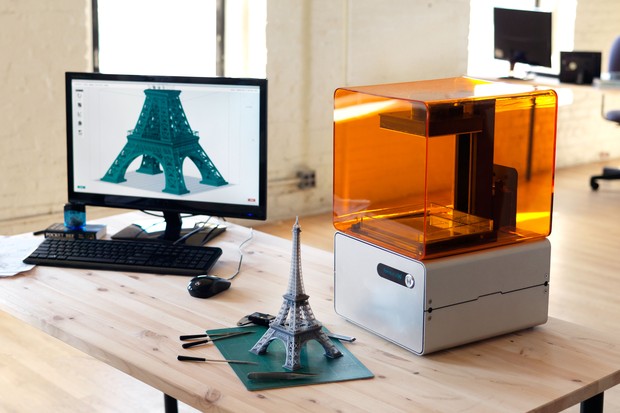
CAD/CAM: Stand for Camputer-Aided Design & Manufacturing, usally refers to softwares that are used for both drawing and manufacturing of a product or model.
-
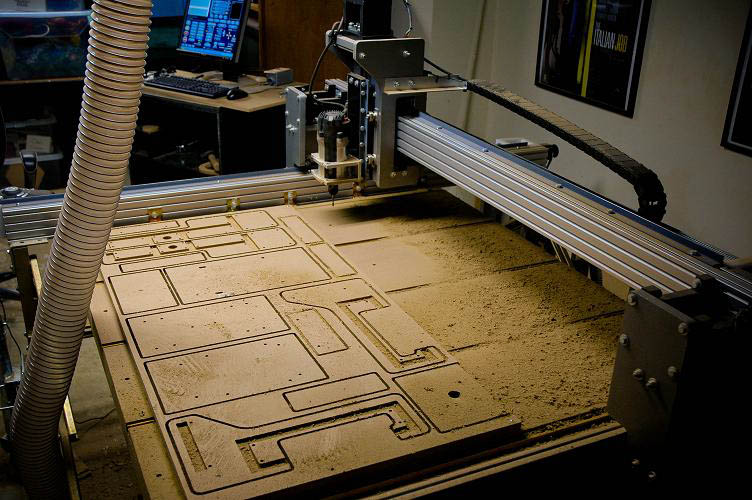
CNC Machine: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) is one in which the functions and motions of a machine tool are controlled by means of a prepared program containing coded alphanumeric data.
- 3D Printing: a process for making a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model, typically by laying down many successive thin layers of a material.
- Laser-Cutting: a technology that uses a laser to cut materials, and is typically used for industrial manufacturing applications.
Sources:
To understand better the use of Digital Fabrication in Architecture, I am reading the book Digital Fabrication, Architectural and Material Technique, of Lisa Iwamoto, that explain in more detail the background of Digital Fabrciation Technologies and present us with some examples of architects that have explored those techniques.